To estimate the amount of profit and assets of any business correctly, we must know how to differentiate between assets that should be depreciated in the accounting books (i.e., depreciable assets) and non-depreciable assets.
Which assets can be depreciated?
Depreciable assets include any physical properties of a business such as machinery and vehicles that:
- Are intended for long term use;
- Have a limited useful life; and
- Are expected to lose their value over their useful lives.
Although a business can use physical properties such as buildings, vehicles, furniture, and equipment for several years, they do not last forever. In accounting, we refer to these assets as depreciable assets.
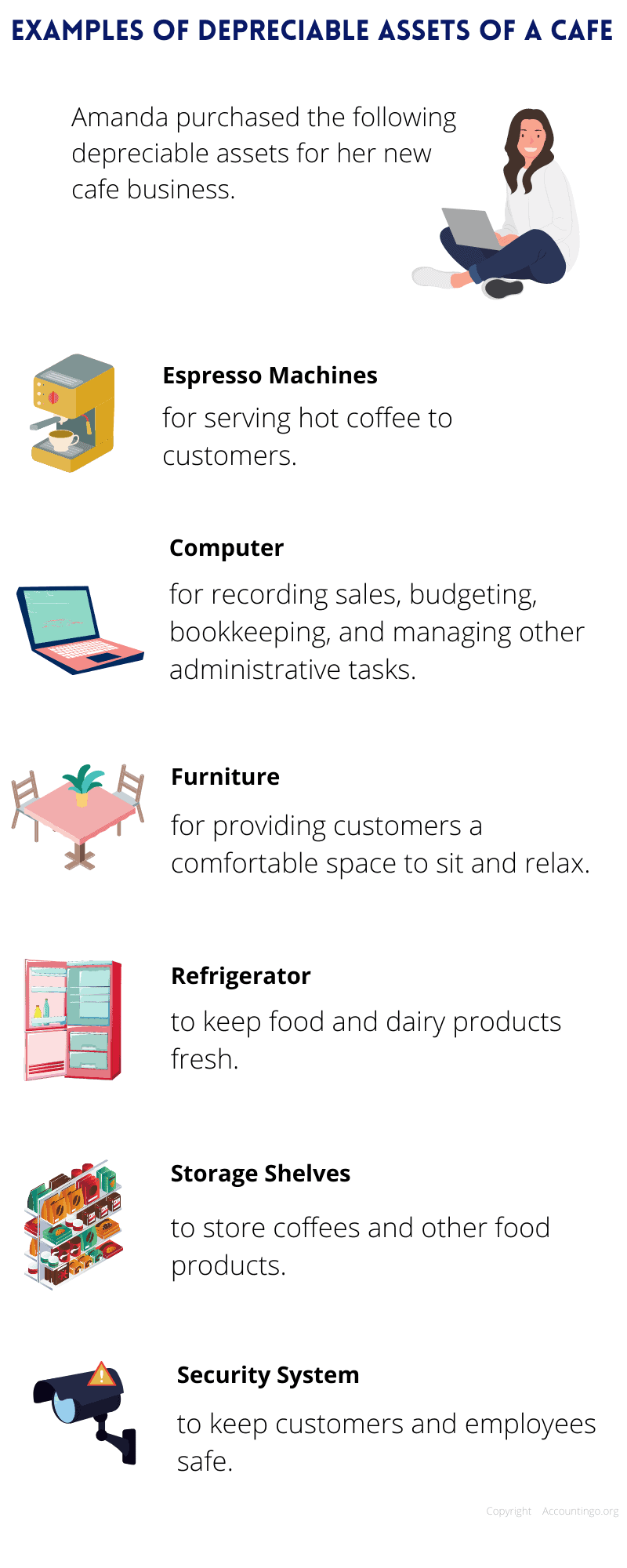
I made the following infographic to give you some examples of depreciable assets in a small business.
If you’re confused about whether you should depreciate an asset or not, look for these five common characteristics of depreciable assets.
5 Characteristics of depreciable assets

Depreciable assets include all tangible fixed assets of a business that can be seen and touched such as buildings, machinery, vehicles, and equipment.
In accounting, we do not depreciate intangible assets such as software and patents. Instead of depreciating such assets, we amortize them which is quite similar to depreciation. But because there are separate accounting rules to consider when applying amortization, most accountants refer to intangible assets as non-depreciable assets.

Depreciable assets are expected to last at least 12 months in the business from when they are acquired.
For example, a restaurant purchases a delivery bike and expects to use it for five years. The delivery bike is a depreciable asset of the restaurant because its expected useful life is more than 12 months from its acquisition.

As you probably know, the basic calculation of depreciation involves dividing the cost of a fixed asset over its useful life using a suitable depreciation method.
So to calculate the depreciation expense, we need to quantify the useful life of the asset mathematically.
For example, library books may last no more than ten years before needing to be replaced with newer editions.
A computer system purchased to run the payroll software may be expected to last only five years before needing replacement to keep up with the updates in the payroll software.
If an asset has an unlimited useful life, such as a piece of land, it is not considered a depreciable asset in accounting. That’s because such assets can be practically used forever without any apparent reduction in value.

In most cases, this means that a business only depreciates those assets that it owns. For example, an airline can depreciate an aircraft that it owns.
However, a business cannot depreciate an asset that it does not effectively own. For instance, if an airline hires an aircraft temporarily in anticipation of a busy season, it should not be considered as a depreciable property of the airline.

The expected value of depreciable assets towards the end of their useful lives is lower than their original cost to the business.
For example, let’s say an animation studio purchased a drawing tablet five years ago for $1000. Today that drawing tablet is worth only $200. The reasons why the drawing tablet has depreciated by $800 in 5 years include:
- The drawing tablet has worn out from having been used all these years.
- Newer drawing tablets with better features are available in the market that are also more efficient and compatible with the latest technology. The current value of the outdated tablet should understandably be lower than that of the newer models.
- Shifts in the animation industry make it necessary for the studio to replace its drawing tablets with newer versions to grow and compete.
Which assets cannot be depreciated?
Short-term assets of a business such as cash, inventory, and receivables are not depreciated in accounting. Non-depreciable assets also include long-term assets such as:
- land;
- investments;
- intangible assets;
- immaterial assets; and
- any personal properties that belong to the owners or employees of the business.
I made the following infographic to explain to you the different types of non-depreciable assets in the context of a small vegetable farm.

Depreciable Assets Quiz
Question 1
Land is an example of a _______________ asset.
Depreciable
Incorrect.
Non-Depreciable
Spot on!
Land is non-depreciable because there is practically no limit to its duration of use.
Question 2
In accounting, cash is considered a depreciable asset because its future worth is reduced because of inflation.
True
Wrong answer.
False
You're right! Current assets such as cash are never depreciable in accounting.
The concept of depreciation in accounting vastly differs from the concept of depreciation in economics. In accounting, we assume the value of cash to remain stable over time and ignore the effects of inflation on monetary assets.
Question 3
Non-Depreciable assets can be short-term or long-term, but depreciable assets only include tangible fixed assets.
True
Correct!
False
Not correct.
Question 4
Which of these assets cannot be depreciated?
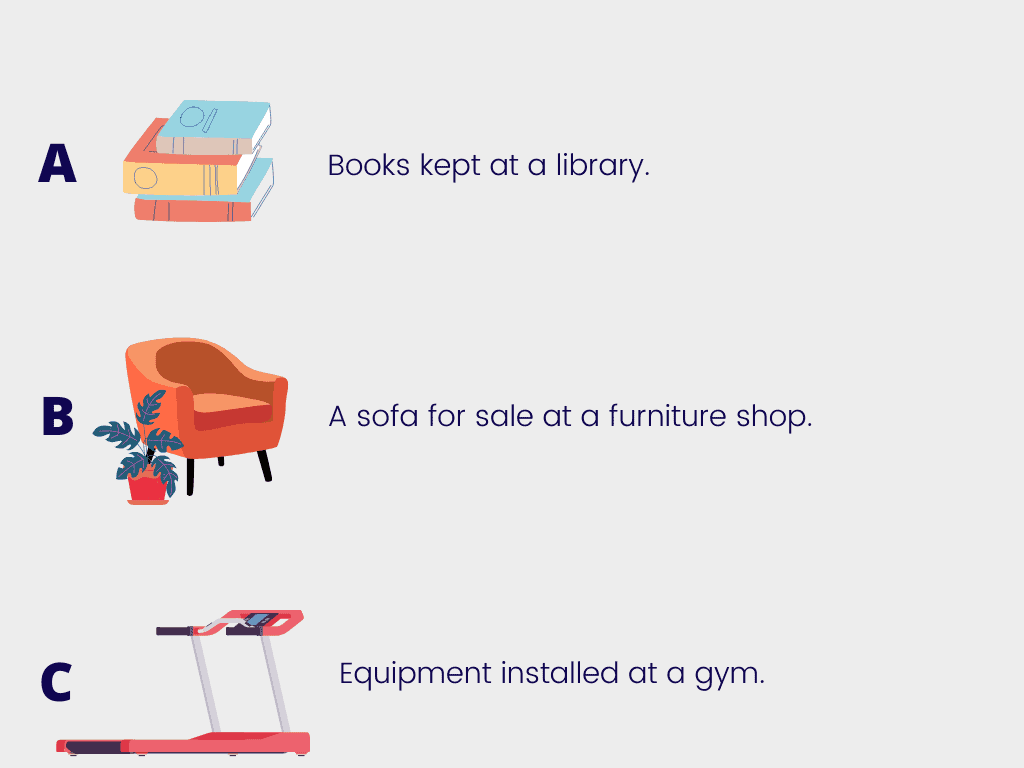
A
Wrong answer.
Library books are depreciable assets with the exception of any rare books that are kept as an investment.
B
Correct!
The sofa is a current asset of the furniture shop because it is for sale which is why it can't be depreciated.
The furniture shop will only depreciate any furniture that is for long-term use and isn't for sale (e.g., a desk in the manager's office).
C
Incorrect.
Question 5
Which of these are depreciable assets in the accounting books of a clothing boutique?

A
You're right!
Mannequins are long-term tangible assets of a clothing boutique which is why they are depreciable in its accounting books.
B
Wrong Answer.
C
Incorrect.
How many questions did you answer correctly?
Score Grade
5 Master
4 Pass